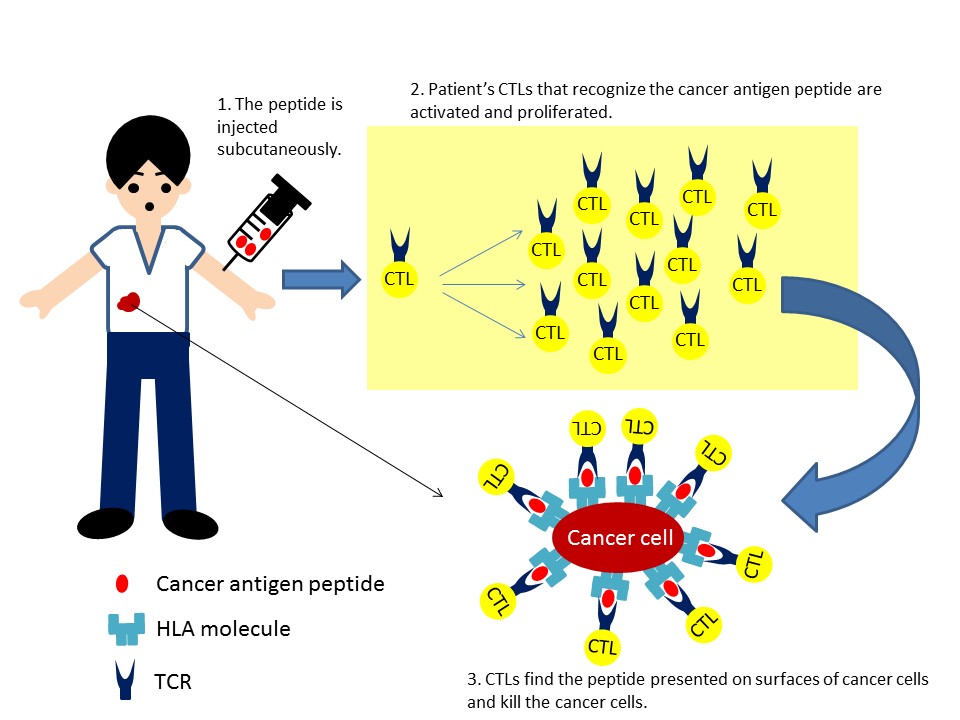
Cancer Peptide Vaccine
Peptide vaccine therapy is an immunotherapy that aims to activate cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) (*1) in patients by inoculating antigen peptides. Cancer cells present antigen peptides (which act as marks of cancer) as complexes with HLA molecules (*2) on their surfaces. Once educated by a peptide vaccine to recognize a certain mark of cancer, CTLs will proliferate to find and kill relevant cancer cells.
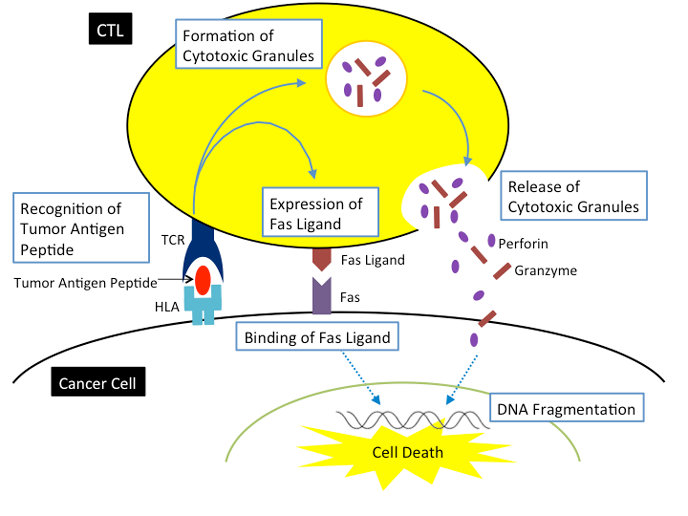
Cytotoxic activity of CTLs against cancer cells
Once CTLs recognize tumor antigen peptides, CTLs release cytotoxic granules and induce Fas/Fas ligand interaction, and then cause cancer cell death by DNA fragmentation.
(*1) Cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL)
Also called killer T cell. It is a lymphocyte that recognizes and kills cancer cells and virus-infected cells.
(*2) HLA molecule
It presents fragments (peptides) of intracellular self and non-self (cancer- or virus-derived) proteins to the cell surface. Various immune responses are caused by T cells recognizing peptides presented by HLA molecules. Polymorphic patterns of HLA genes are different depending on countries and ethnic groups. About six out of ten people in Japan have the HLA-A*24:02 type.
